What does EDFA mean? What is the full form of EDFA?
The Full Form of EDFA is Erbium-doped fiber amplifier.
Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) is an optical amplifier used in the C-band and L-band, where loss of telecom optical fibers becomes lowest in the entire optical telecommunication wavelength bands. Invented in 1987 [1], EDFA is now most commonly used to compensate the loss of an optical fiber in long-distance optical communication. Another important cha
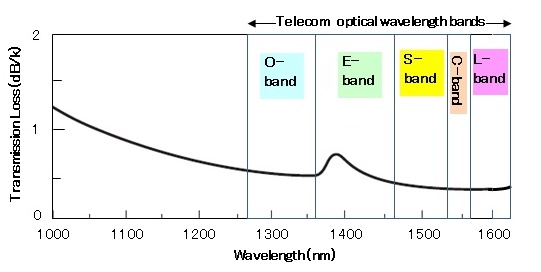
about-telecom-band
acteristic is that EDFA can amplify multiple optical signals simultaneously, and thus can be easily combined with WDM technology.
EDFAs are used as a booster, inline, and pre-amplifier in an optical transmission line, as schematically shown in Figure 2. The booster amplifier is placed just after the transmitter to increase the optical power launched to the transmission line. The inline amplifiers are placed in the transmission line, compensating the attenuation induced by the optical fiber. The pre-amplifier is placed just before the receiver, such that sufficient optical power is launched to the receiver. A typical distance between each of the EDFAs is several tens of kilometers.
Before the invention of EDFA, a long optical fiber transmission line required a complicated optical-to-electrical (O-E) and E-O converter for signal regeneration. The use of EDFA has eliminated the need for such O-E and E-O conversion, significantly simplifying the system. This is especially of use in a submarine optical transmission, where more than a hundred EDFA repeaters may be needed to construct one link. The TPC-5CN (Trans-Pacific Cable 5 Cable Network), started its operation in 1996, is the first submarine optical fiber network which employed EDFA.
EDFA
means
Erbium-doped fiber amplifier![]()
Translate Erbium-doped fiber amplifier to other language.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.