What does SVC mean? What is the full form of SVC?
The Full Form of SVC is Switched Virtual Circuit.
Switched Virtual Circuit, also known as SVC, is a form of telecommunications service that provides a path between two nodes in a packet-switched network. The path is set up and configured at the beginning of a session and is dismantled at the end. Each new session requires a switching path to be established, and this path differs during each session depending on the available switches.
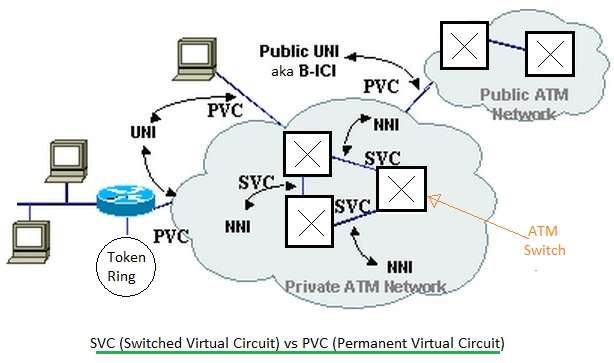
SVC-vs-PVC
The Full Form of SVC is Switched Virtual Circuit.
Scalable Video Coding: (SVC) is the name for the Annex G extension of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video compression standard. SVC standardizes the encoding of a high-quality video bitstream that also contains one or more subset bitstreams (a form of layered coding). A subset video bitstream is derived by dropping packets from the larger video to reduce the bandwidth required for the subset bitstream. The subset bitstream can represent a lower spatial resolution (smaller screen), lower temporal resolution (lower frame rate), or lower quality video signal. H.264/MPEG-4 AVC was developed jointly by ITU-T and ISO/IEC JTC 1. These two groups created the Joint Video Team (JVT) to develop the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard.
SVC (Scalable Video Coding) technology allows transferring several substream of different quality in one stream. As a rule these streams are basic and secondary ones. The basic stream is transferred in standard quality, while the secondary one – in the enhanced quality, for example, with higher frame rate or video resolution.
SVC enables video conferencing server adjust video stream to the varying characteristics of the endpoint terminals: CPU capabilities and bandwidth. The server sets the specific stream type for each device: endpoints with high bandwidth decode the whole stream, while endpoints with low bandwidth or device (mobile phones and tablets) receive only the basic stream with lower data transfer rate. In other words, “weaker” participants don’t influence video quality other participant receive during the conference.
Without SVC all multipoint conference participants receive video stream of the quality satisfactory for the device with the weakest characteristics. From now all multipoint conference participants will receive the image quality maximum possible for the equipment and network channels they use.
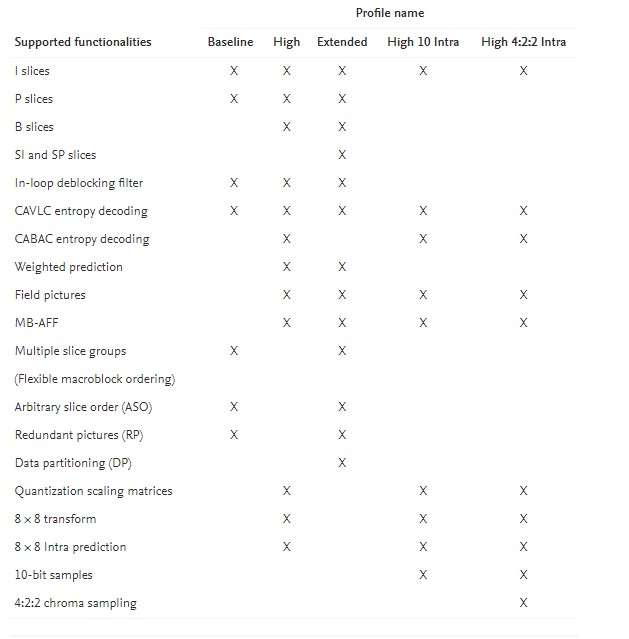
Similar to other standards, H.264/AVC defines a set of “profiles” that each support only a subset of the entire syntax of the standard and are designed to target specific application areas. The Baseline Profile targets applications not requiring interlace support and requiring moderate computational complexity, such as videoconferencing and mobile. This profile also provides robustness for use on unreliable channels, where some of the video data may be lost or corrupted. The High Profile targets applications such as broadcast of standard-definition (SD) and high-definition (HD) video on more reliable channels, and storage on optical media. This profile includes more advanced coding tools, such as CABAC entropy coding and B slices, that can improve compression capability over that provided by the Baseline Profile, at the cost of higher complexity. The Main Profile contains a subset of the features of the High Profile—it is now primarily only of historical relevance after the development of the High Profile. The Extended Profile is intended for use in streaming and use in error prone transmission environments, such as wireless networks—although it has not been widely adopted.
A number of profiles have been defined for higher quality, more “professional”, usage applications. The High 10, High 4:2:2, and High 4:4:4 Predictive profiles fall in this category. The High 10 Profile permits up to 10-bit sample precision; the High 4:2:2 Profile further permits both 4:2:0 and 4:2:2 chroma samplings; and the High 4:4:4 Predictive Profile also supports up to 14-bit samples and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. For production and contribution applications such as professional high-definition video acquisition and editing, the interpicture prediction feature is less necessary, and to target these applications the corresponding High 10 Intra, High 4:2:2 Intra, High 4:4:4 Intra, and CAVLC 4:4:4 Intra profiles have been specified. (The CAVLC Intra Profile is similar to the High 4:4:4 Intra Profile, but omits support of CABAC entropy coding to reduce computational complexity.) Since there is no interpicture prediction loop in the Intra-only profiles, and since these profiles are intended for applications that typically avoid significant artifacts, the deblocking filter is not normatively required for their decoding.
Three SVC profiles have also been specified, which are the Scalable Baseline, Scalable High, and Scalable High Intra profiles.9
The key features that are supported by some of these profiles10 of H.264/AVC are shown in Table 10.2.
SVC
means
Switched Virtual Circuit![]()
Translate Switched Virtual Circuit to other language.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.