Phenomena vs. Phenomenon: A Linguistic Guide to Keep It Singular or Plural
Phenomena vs. Phenomenon: Understanding the Key Differences When it comes to discussing occurrences or events, the words “phenomena” and “phenomenon” are often used interchangeably. However, there is a
The Difference Between Pet and Petted
History: The word “pet” originated from the Anglo-Norman French word “petit,” meaning small or little. “Petted,” on the other hand, is the past tense and past participle form of the verb
Understanding the Difference Between Perspective and Prospective
Perspective vs. Prospective Perspective History: The word “perspective” originated from the Latin word “perspectus,” which means “clearly perceived or understood.” It first appeared in the
The Distinction Between Personal vs. Personnel
The Difference Between Personal vs. Personnel Personal and personnel are two words that are often confused due to their similar spellings but have very different meanings. Understanding the distinction between these two words
The Distinction Between Per cent and Percent
The Difference Between Per cent and Percent History of the Words The words “per cent” and “percent” both originated from the Latin phrase “per centum,” which means “by the
The Distinction Between People and Persons
The Difference Between People and Persons History: The words “people” and “persons” both have roots in Old English, but they have evolved differently in terms of usage over time. “People”
Understanding the Difference Between People and Person
People vs. Person The English language can be confusing at times, and two commonly used words that often lead to mix-ups are ‘people’ and ‘person’. While they both refer to individuals, there
Peal vs. Peel: Understanding the Difference
Peal vs. Peel: Understanding the Difference The English language is full of words that look or sound similar but have completely different meanings. Two such words that often cause confusion are “peal” and
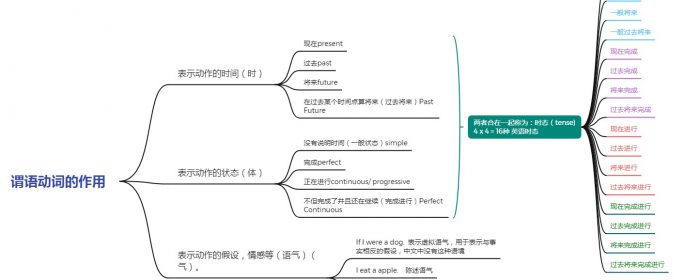
一文搞懂英语的16种时态
谓语动词有3大作用 1,表示动作的时间(时): 现在present,过去past,将来future,在过去某个时间点算将来(过去将来)Past Future 2,表示动作的状态(体):没有说明时间(一般状态)simple,完成perfect,正在进行continuous/ progressive,不但完成了并且还在继续(完成进行)Perfect Continuous 以上两者合在一起称为:时间(tense)
一文搞懂美语的发音技巧之-节奏
很多人认为说英语只要把单词发准了,再模仿一下美国人说话的调调就可以了, 这是不够的 还有一个很重要的东西:节奏(rhythm) 节奏没有把握好,是说不好英语的最最重要的原因 可能你会觉得,节奏有什么关系,每个单词读好,再把单词连在一起读不就可以 了吗? 错 语言的等时性(isochrony) 普通话: 每个字是一个音节,一个音节接一个音节读就行了 所以: 普通话的每一个音节的时间基本相等 (音节等时)(和法法相似)
一文搞懂美语的发音技巧之-连续,弱读
先看几个单词: to go to(兔) school at look at(艾特) me but sad but(爸特) true can I can(看) do it 美国人是这样读的 to /tə/ at /ət/ but /bət/ can /kən/ 中央元音 neutual vowel [ə] 最重要的元音 这种读音方式也称为: weak form (弱读) 注意:弱读不是轻声的读,
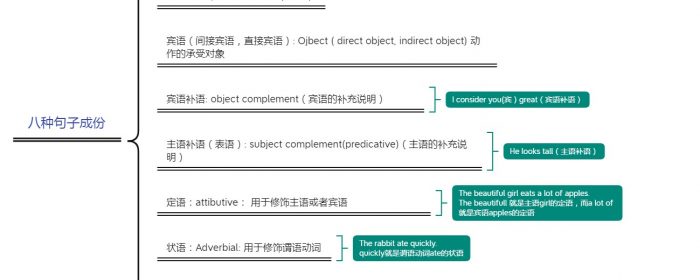
一文搞懂英语的语法体系-5种基本句型,8种句子成份,10种词类,谓语动词,英语时态
你现在英语语法体系和框架是否有认知? 我们为什么学语法? 语法只有一个目的:造句。 我们平时的文章是有些是短句子,有些是由短句子组成的长句子。但长句子并不适合做语法讨论,我们只能把长句子拆成短句直到不能再拆(基本句),这样来讨论语法 长句子就是基本句(simple sentence)的组合 句子成份:part of speech 当英语的句子拆到不能再拆时就变成最基本的句子,它们总是在表达:什么。。。怎么样。。。: 句子的基本成份: 什么 怎么样